How Bidencash Is Making Identity Theft Easier with CC and Bins Listings
Introduction to Bidencash and its Controversy
In a computerized scene where comfort frequently bests alert, Bidencash has arisen as a dubious figure. This stage guarantees speedy and simple exchanges however creates shaded areas of uncertainty over its safety efforts. As conversations about fraud become stronger, many are left pondering: is Bidenscash.cc simply an imaginative monetary instrument or a passage to expanded weakness?
With murmurs of Mastercard (CC) data and Receptacles postings coursing in obscurity corners of the web, it’s crucial for plunge profound into how this help works — and how that affects you. How about we disentangle the layers encompassing Bidencash and investigate its suggestions on our own security in the present tech-driven world.
The Connection Between CC and Bins Listings
CC and Canisters postings are interconnected such that earns consideration from those engaged with illegal exercises. CC, or Visa numbers, can be utilized to make unapproved exchanges. In the interim, Receptacles, which allude to Bank Recognizable proof Numbers, assist with distinguishing the establishment that gave the card.
At the point when people gain a rundown of substantial Containers, they can undoubtedly coordinate it with taken CC subtleties. This matching considers consistent exchanges without raising prompt warnings.
The accessibility of such records online has simplified it for personality cheats to work undetected. They exploit these associations with make fake cards or perform online misrepresentation.
As cybercriminals become savvier, understanding this association is critical for the two shoppers and organizations planning to shield their monetary data from falling into some unacceptable hands.
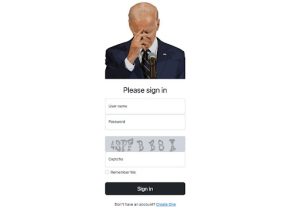
A Screenshot of Bidencash (bidenscash.cc) login page
How Bidencash Facilitates Identity Theft
Bidencash works in a shadowy domain, giving admittance to compromised Visas and Receptacles. This stage has arisen as a center for those looking for unlawful monetary profit.
The simplicity of getting delicate data is disturbing. Clients can rapidly peruse postings that contain taken card subtleties, making it perilously basic for character criminals to carry out extortion.
With insignificant confirmation processes, Bidencash permits people with vindictive expectation to complete exchanges without the requirement for broad historical verifications. This absence of oversight makes a favorable place for crime.
In addition, its easy to understand interface draws in prepared crooks as well as unpracticed people hoping to bring in speedy cash. The outcome? An expansion in data fraud cases influencing endless casualties who accidentally succumb to these plans.
Related: Jokerstash
The Impact of Bidencash on Individuals and Businesses
Bidenscash.cc has made waves across the internet based monetary scene. Its administrations are engaging, yet the ramifications raise concerns.
People face elevated dangers of fraud. Individual information can without much of a stretch be taken advantage of through CC and Receptacles postings. Casualties frequently end up in a tangled trap of monetary extortion, bringing about destroyed FICO ratings and close to home pain.
For organizations, the stakes are similarly high. Fake exchanges lead to critical misfortunes and harmed notorieties. Organizations should put additional in safety efforts to safeguard delicate data from being compromised.
Additionally, client trust can disintegrate quickly when word gets out about breaks connected to stages like Bidencash login. The gradually expanding influences influence deals and brand reliability as buyers become careful about advanced exchanges out and out.
Exploring this new reality requires cautiousness on all fronts — both individual clients and associations need to adjust rapidly to these arising dangers.
Steps to Protect Yourself from Identity Theft
Protecting yourself from identity theft starts with vigilance. Regularly check your financial statements for any unauthorized transactions. Early detection can save you a lot of trouble.
Next, consider using strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts. Password managers can help generate and store these securely. Avoid sharing sensitive information over public Wi-Fi networks to minimize risk.
Consider freezing your credit if you’re particularly concerned about potential threats. This action prevents new accounts from being opened in your name without permission.
Be cautious when sharing personal information online or through social media platforms. Scammers often harvest data from seemingly innocent profiles.
Invest in identity theft protection services that offer monitoring and recovery assistance. These tools provide an extra layer of security as they keep watch on suspicious activities related to your identity.
Alternatives to Using Bidencash for Financial Transactions
On the off chance that you’re thinking about options in contrast to Bidencash cc for monetary exchanges, a few secure choices exist. Advanced wallets like PayPal and Venmo offer easy to understand interfaces while focusing on security.
Cryptographic forms of money have acquired prominence as decentralized strategies for installment. Stages, for example, Coinbase or Binance permit clients to execute without conventional banks, adding an additional layer of protection.
For the people who favor traditional banking, administrations like Zelle or direct bank moves give a solid method for sending cash. They are frequently connected straightforwardly to your financial balance, limiting dangers related with outsider stages.
Pre-loaded charge cards can likewise be a protected decision. They let you load just the sum you wish to spend, decreasing openness in the event of misrepresentation.
Picking these choices improves your security as well as cultivates more command over your monetary exchanges in the present advanced scene.
Conclusion: Staying Safe in the Digital Age
As we explore the intricacies of the computerized age, remaining educated and cautious about our own data is vital. Bidencash has opened an entryway for people looking for illegal ways of taking advantage of monetary frameworks, making it more straightforward than at any other time for wholesale fraud to flourish.
Being proactive in safeguarding yourself against data fraud is fundamental. Use devices, for example, credit checking administrations and two-factor confirmation whenever the situation allows. Consistently check your bank articulations and credit reports for any indications of unapproved movement.
Consider options in contrast to utilizing stages like Bidenscash.cc that might think twice about security. There are more secure monetary exchange techniques accessible that focus on client insurance while additionally guaranteeing accommodation.
The scene of online exchanges keeps on advancing, introducing the two amazing open doors and dangers. Embracing best practices in network safety can assist with defending your data in an undeniably computerized world. Remain instructed, remain alert, and safeguard what makes the biggest difference — your personality.



